目錄表
國立屏東大學 資訊工程系 Java物件導向程式設計
Java與關聯式資料庫
本文將說明如何在Java語言裡,將物件儲存至關聯式資料庫(Relational Database Systems,RDBS)中。
JDBC
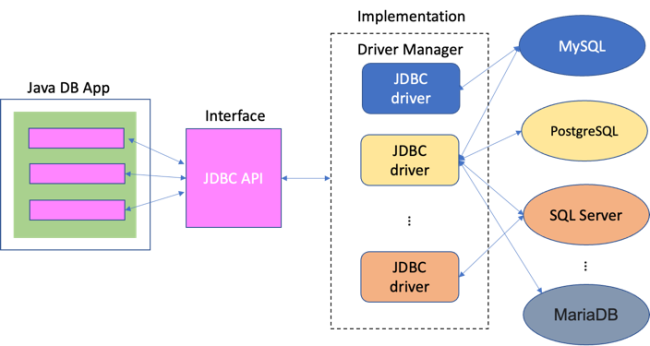
JDBC全名為Java Database Connectivity,是Java語言用以連接存取不同資料庫系統的一致性開放介面 — 換句話說,只要使用JDBC的方式,將可以連上許多不同的資料庫系統。事實上,JDBC只是一組以介面(interface)方式存在的API,規範了程式該使用何種方法(呼叫特定的method)連接及存取資料庫,經由資料庫開發者或第三方所實作(implement)的驅動程式(driver)來完成實際對特定資料庫系的操作,請參考figure 1所顯示的概觀。
關於JDBC API(也就是interface)的文件,可以參考官方的說明文件(javadoc),以下筆者就重要的相關method進行說明:
連接資料庫系統
我們可以透過java.sql.DriverManager來建立和資料庫的連接,其傳回值為java.sql.Connection。
java.sql.Connection con=null;
try
{
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //註冊driver
con = java.sql.DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://web.csie2.nptu.edu.tw/junwu_test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=Big5",
"username","password");
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e) //驅動程式不存在時會產生ClassNotFoundException
{
System.out.println("DriverClassNotFound :"+e.toString());
}
catch(java.sql.SQLException x) //有可能會產生sqlexception
{
System.out.println("Exception :"+x.toString());
}
為了要能正確地執行上述程式以完成對系計中MySQL資料庫系統的連接,我們必須為專案增加對應的JDBC driver — mysql-connector-java-5.0.8,請自行下載後依下列步驟加入專案:
- 在專案名稱上按滑鼠右鍵,選擇「Properties」以開啟「Properties」對話窗。
- 在左側的導覽樹中點選「Java Build Path」。
- 選擇「Libraries」,並選取「classpath」。
- 按下「Add External Jars」並選擇加入jar檔。
同學可以使用phpMyAdmin,來管理資料庫。
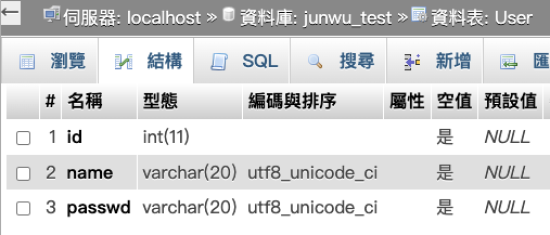
關於此範例所使用到的User表格的綱要可參考figure 2:
建立Table
String createTAB_SQL = "CREATE TABLE User (id INTEGER, name VARCHAR(20), passwd VARCHAR(20))";
java.sql.Statement stat = null;
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
stat.executeUpdate(createTAB_SQL);
}
catch(java.sql.SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Create Table Exception :" + e.toString());
}
新增資料
java.sql.PreparedStatement pst=null;
String insert_SQL = "insert into User(id,name,passwd) values (?, ?, ?)";
int id=0;
try
{
pst = con.prepareStatement(insert_SQL);
pst.setInt(1, id++);
pst.setString(2, "someone");
pst.setString(3, "secret");
pst.executeUpdate();
}
catch(java.sql.SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Insert Exception :" + e.toString());
}
刪除表格
java.sql.Statement stat = null;
String dropTAB_SQL = "DROP TABLE User";
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
stat.executeUpdate(dropTAB_SQL);
}
catch(java.sql.SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Drop Table Exception :" + e.toString());
}
查詢資料
java.sql.Statement stat = null;
java.sql.ResultSet rs = null;
String selectSQL="select * from User";
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
rs = stat.executeQuery(selectSQL);
System.out.println("ID\t\tName\t\tPASSWORD");
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t\t"+
rs.getString("name")+"\t\t"+
rs.getString("passwd"));
}
}
catch(java.sql.SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Selection Exception :" + e.toString());
}
關閉連接及相關物件
使用完資料庫後,記得要關閉相關物件,才不會在資料庫系統因逾時(timeout)而中斷連接前,發生其它連接的錯誤狀況。註:此部份的程式碼,可以寫在前述的資料庫操作的try敘述後的finally敘述裡。
try
{
if(rs!=null)
{
rs.close();
rs = null;
}
if(stat!=null)
{
stat.close();
stat = null;
}
if(pst!=null)
{
pst.close();
pst = null;
}
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Close Exception :" + e.toString());
}
範例
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JDBCMySQL test = new JDBCMySQL();
test.dropTable();
test.createTable();
test.insertTable(101, "王大明", "12356");
test.insertTable(102, "Jackson", "7890");
test.SelectTable();
}
}
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCMySQL {
private Connection con = null;
private Statement stat = null;
private ResultSet rs = null;
private PreparedStatement pst = null;
private String dropTAB_SQL = "DROP TABLE User ";
private String createTAB_SQL = "CREATE TABLE User (" +
" id INTEGER " +
" , name VARCHAR(20) " +
" , passwd VARCHAR(20))";
private String insert_SQL = "insert into User(id,name,passwd) values(?, ?, ?)";
private String select_SQL = "select * from User ";
public JDBCMySQL()
{
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
con = DriverManager.getConnection(
"jdbc:mysql://web.csie2.nptu.edu.tw/YOURDBNAME?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=Big5",
"USERNAME","PASSWORD");
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println("DriverClassNotFound :"+e.toString());
}
catch(SQLException x) {
System.out.println("Exception :"+x.toString());
}
finally
{
close();
}
}
public void createTable()
{
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
stat.executeUpdate(createTAB_SQL);
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Create Table Exception :" + e.toString());
}
finally
{
close();
}
}
public void insertTable( int id, String name,String passwd)
{
try
{
pst = con.prepareStatement(insert_SQL);
pst.setInt(1, id);
pst.setString(2, name);
pst.setString(3, passwd);
pst.executeUpdate();
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Insert Exception :" + e.toString());
}
finally
{
close();
}
}
public void dropTable()
{
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
stat.executeUpdate(dropTAB_SQL);
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("DropDB Exception :" + e.toString());
}
finally
{
close();
}
}
public void SelectTable()
{
try
{
stat = con.createStatement();
rs = stat.executeQuery(select_SQL);
System.out.println("ID\t\tName\t\tPASSWORD");
while(rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getInt("id")+"\t\t"+
rs.getString("name")+"\t\t"+rs.getString("passwd"));
}
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Selection Exception :" + e.toString());
}
finally
{
close();
}
}
private void close()
{
try
{
if(rs!=null)
{
rs.close();
rs = null;
}
if(stat!=null)
{
stat.close();
stat = null;
}
if(pst!=null)
{
pst.close();
pst = null;
}
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
System.out.println("Close Exception :" + e.toString());
}
}
}
此程式的執行結果如下:
ID Name PASSWORD 101 王大明 12356 102 Jackson 7890
Hibernate
JPA
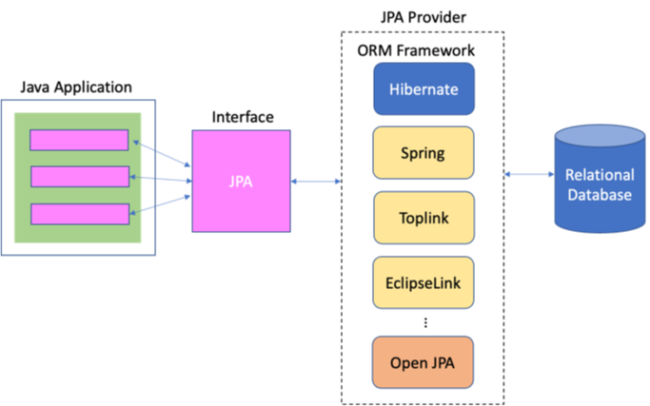
JPA的全名為Java Persistence API,是用來規範物件/關聯對映(Object-Relational Mappling,ORM)實作的介面,其目的在於幫助程式設計師將程式執行階段的物件實體儲存到資料庫系統裡 — 又稱為持久化(persistence)。請參考figure 3所顯示的概觀:
如figure 3所示,JPA並不是直接用以存取資料庫,而就如同JDBC一樣,只是一個介面用以規範對資料庫進行的物件存取;真正的功能是透過JPA Provider來完成的,而ORM Framework就是JPA Provider的實作。目前常見可用於JPA Provider的ORM Framework包含Hibernate、Spring、Toplink、Eclipselink、Open JPA等。
儘管JPA的想法和JDBC很類似,但它們是不相同的 — JDBC是在程式中使用API存取資料庫裡的資料,JPA則是在程式中使用API來存取在ORM Framework裡的物件,而ORM Framework會自己想辦法將物件的操作轉換為對關聯式資料庫的操作。另外,JPA使用Java Persistence Query Language(Java持久化查詢語言,JPQL)來對ORM Framework下達操作命令,避免了JDBC使用SQL語言進行操作 — 但不同資料庫系統的SQL語法並不完全相同,所以使用JDBC時,常常必須針對不同的資料庫修改程式碼中的SQL命令。
JPA主要有註解(annotation)與XML組態檔等兩種用法,可以將程式執行時的物件實體持久化到資料庫理。本文後續將針對Hibernate進行說名與示範。由於Hibernate較多人使用的是5.0版本,因此本人將先針對5.0加以說明,並再最後提供一個6.0的新版本示範。
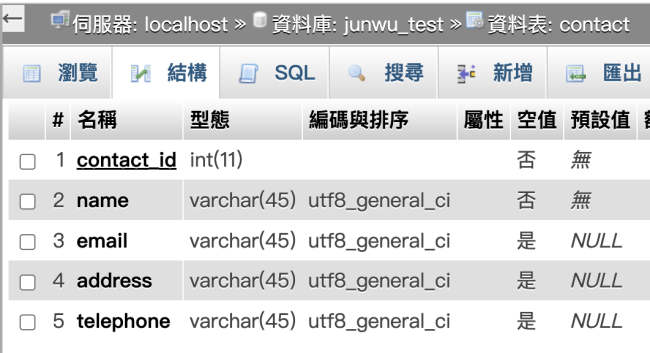
另外,請注意,以下的範例必須使用一個名為contact的表格,請自行參考建立:
Hibernate 5 (Annotation)
執行以下範例所需的Libraries已上傳到Teams,請自行下載並加入專案。
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Environment;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
/** This example is modified from www.codejava.net, thanks for their great work!
*
* A sample program that demonstrates how to perform simple CRUD operations
* with Hibernate framework.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class ContactManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// loads configuration and creates a session factory
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
Properties settings = new Properties();
settings.put(Environment.DRIVER, "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
settings.put(Environment.URL, "jdbc:mysql://web.csie2.nptu.edu.tw:3306/DB_NAME");
settings.put(Environment.USER, "USERNAME");
settings.put(Environment.PASS, "PASSWORD");
settings.put(Environment.SHOW_SQL, "true");
configuration.setProperties(settings);
configuration.addAnnotatedClass(Contact.class);
ServiceRegistry registry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(registry);
// opens a new session from the session factory
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
// persists one new Contact objects
/*
Contact contact1 = new Contact(1, "Haina Tu", "hainatu@gmail.com", "TWTW", "0904277091");
session.persist(contact1);
*/
/*
Contact contact2 = new Contact("NewTestNam", "hainatu@gmail.com", "TWTW", "0904277091");
session.persist(contact2);
*/
/*
Contact contact3 = new Contact(3, "Bill", "bill@gmail.com", "USA", "18001900");
Serializable id = session.save(contact3);
System.out.println("created id: " + id);
*/
/*
// loads a new object from database
Contact contact4 = (Contact) session.get(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
if (contact4 == null) {
System.out.println("There is no Contact object with id=1");
} else {
System.out.println("Contact4's name: " + contact4.getName());
}
*/
/*
// loads an object which is assumed exists
Contact contact5 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
System.out.println("Contact5's name: " + contact5.getName());
*/
/*
// updates a loaded instance of a Contact object
Contact contact6 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
contact6.setEmail("info1@company.com");
contact6.setTelephone("1234567890");
session.update(contact6);
*/
/*
// deletes a loaded instance of an object
Contact contact7 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
session.delete(contact7);
*/
/*
// deletes an object
Contact contact8 = new Contact();
contact8.setId(8);
contact8.setName("Innoce");
session.save(contact8);
// session.delete(contact8);
*/
// select all contacts
Query<Contact> query=session.createQuery("from Contact");
List<Contact> list=query.list();
for(Contact c: list)
{
System.out.println("id=" + c.getId() + " name=" + c.getName() );
}
// commits the transaction and closes the session
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="contact")
public class Contact {
@Id
@Column(name="contact_id")
private int id;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@Column(name="email")
private String email;
@Column(name="address")
private String address;
@Column(name="telephone")
private String telephone;
public Contact() {
}
public Contact(int id, String name, String email, String address,
String telephone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public Contact(String name, String email, String address, String telephone) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
}
Hibernate 5(使用XML對映檔案)
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
public class Contact {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String address;
private String telephone;
public Contact() {
}
public Contact(int id, String name, String email, String address,
String telephone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public Contact(String name, String email, String address, String telephone) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
}
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<!-- Database connection settings -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://web.csie2.nptu.edu.tw:3306/DB_NAME</property>
<property name="connection.username">USERNAME</property>
<property name="connection.password">PASSWORD</property>
<property name="connection.useUnicode">true</property>
<property name="connection.characterEncoding">UTF-8</property>
<property name="connection.charSet">UTF-8</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="tw/edu/nptu/resl/Contact.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="tw.edu.nptu.resl">
<class name="Contact" table="contact">
<!--
<id name="id" column="contact_id">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
-->
<id name="id" column="contact_id"/>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name"/>
<property name="email" />
<property name="address"/>
<property name="telephone"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistry;
//import org.hibernate.service.ServiceRegistryBuilder; deprecated since Hibernate 4.3.4
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
/** This example is modified from www.codejava.net, thanks for their great work!
*
* A sample program that demonstrates how to perform simple CRUD operations
* with Hibernate framework.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class ContactManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// loads configuration and creates a session factory
Configuration configuration = new Configuration().configure();
configuration.addClass(Contact.class);
ServiceRegistry registry = new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().applySettings(configuration.getProperties()).build();
SessionFactory sessionFactory = configuration.buildSessionFactory(registry);
// opens a new session from the session factory
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
// persists two new Contact objects
Contact contact1 = new Contact(1, "Nam", "hainatu@gmail.com", "Vietnam", "0904277091");
session.persist(contact1);
Contact contact2 = new Contact(2, "Bill", "bill@gmail.com", "USA", "18001900");
Serializable id = session.save(contact2);
System.out.println("created id: " + id);
// loads a new object from database
Contact contact3 = (Contact) session.get(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
if (contact3 == null) {
System.out.println("There is no Contact object with id=1");
} else {
System.out.println("Contact3's name: " + contact3.getName());
}
// loads an object which is assumed exists
Contact contact4 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(2));
System.out.println("Contact4's name: " + contact4.getName());
// updates a loaded instance of a Contact object
Contact contact5 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
contact5.setEmail("info1@company.com");
contact5.setTelephone("1234567890");
session.update(contact5);
// updates a detached instance of a Contact object
Contact contact6 = new Contact(3, "Jobs", "jobs@applet.com", "Cupertino", "0123456789");
session.save(contact6);
// deletes an object
Contact contact7 = new Contact();
contact7.setId(7);
contact7.setName("Innoce");
session.save(contact7);
session.delete(contact7);
contact1.setName("Another");
// deletes a loaded instance of an object
Contact contact8 = (Contact) session.load(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(3));
session.delete(contact8);
// commits the transaction and closes the session
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
Hibernate 6(使用XML對映檔案)
Hibernate目前最新版為6,所以前述的方法有許多不相同的地方,在類別庫的部份也有所不同,請自行前往Teams下載。 以下為使用XML對映檔案的範例程式:
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
public class Contact {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String address;
private String telephone;
public Contact() {
}
public Contact(int id, String name, String email, String address,
String telephone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public Contact(String name, String email, String address, String telephone) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.address = address;
this.telephone = telephone;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getTelephone() {
return telephone;
}
public void setTelephone(String telephone) {
this.telephone = telephone;
}
}
<persistence xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_2_0.xsd"
version="2.0">
<persistence-unit name="tw.edu.nptu.resl.contact">
<description>
Persistence unit for the Jakarta Persistence tutorial of the Hibernate Getting Started Guide
</description>
<class>tw.edu.nptu.resl.Contact</class>
<properties>
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.url" value="jdbc:mysql://web.csie2.nptu.edu.tw:3306/DB_NAME" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.user" value="USERNAME" />
<property name="jakarta.persistence.jdbc.password" value="PASSWORD" />
<property name="hibernate.show_sql" value="true" />
<!-- <property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="create" /> -->
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping package="tw.edu.nptu.resl">
<class name="Contact" table="contact">
<!--
<id name="id" column="contact_id">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
-->
<id name="id" column="contact_id"/>
<property name="name" type="string" column="name"/>
<property name="email" />
<property name="address"/>
<property name="telephone"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
package tw.edu.nptu.resl;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import jakarta.persistence.Persistence;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityManager;
/** This example is modified from www.codejava.net, thanks for their great work!
*
* A sample program that demonstrates how to perform simple CRUD operations
* with Hibernate framework.
* @author www.codejava.net
*
*/
public class ContactManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SessionFactory sessionFactory = (SessionFactory) Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory( "tw.edu.nptu.resl.contact" );
EntityManager entityManager = sessionFactory.createEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Contact contact1 = new Contact(112, "Haina Tu", "hainatu@gmail.com", "Vietnam", "0904277091");
entityManager.persist(contact1);
Contact c=entityManager.find(Contact.class, Integer.valueOf(1));
System.out.println(c.getName());
List<Contact> result = entityManager.createQuery( "from Contact where id > '0'", Contact.class ).getResultList();
for ( Contact ct : result ) {
System.out.println( "Contact (" + ct.getName() + ") " );
}
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
}
}